Fibroid vs Endometriosis: Symptoms, Causes & Treatment in Aundh
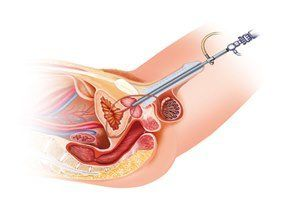
Chronic pelvic pain can be exhausting, especially when you aren’t sure what’s causing it. If you are struggling with heavy periods or persistent discomfort, you might be searching for a fibroid endometriosis surgeon in Aundh to get a clear diagnosis. Both uterine fibroids and endometriosis are common reproductive health issues, but they require very different approaches for treatment. Understanding the Difference: Fibroids vs. Endometriosis While both conditions affect the female reproductive system and can cause intense pain, they are fundamentally different in how they develop. What are Uterine Fibroids? Fibroids are non-cancerous growths that develop in or on the muscular walls of the uterus. They are essentially firm, compact tumors made of smooth muscle cells and fibrous connective tissue. What is Endometriosis? Endometriosis occurs when tissue similar to the lining of the uterus (the endometrium) grows outside the uterus. This tissue can be found on the ovaries, fallopian tubes, or the outer surface of the uterus, causing inflammation and scarring. Key Symptoms to Watch For Many women in Aundh suffer in silence because the symptoms of these two conditions often overlap. However, a skilled fibroid endometriosis surgeon in Aundh can help distinguish between the two based on your specific pain patterns. Symptoms of Fibroids: Heavy Menstrual Bleeding: Often involving large blood clots. Pelvic Pressure: A feeling of fullness or heaviness in the lower abdomen. Frequent Urination: Large fibroids can press against the bladder. Enlarged Abdomen: Some fibroids grow large enough to mimic a pregnancy. Symptoms of Endometriosis: Deep Pelvic Pain: Especially during menstruation or intercourse. Chronic Lower Back Pain: Persistent aching that worsens during your period. Painful Bowel Movements: Often occurring during the menstrual cycle. Infertility Issues: Many women discover they have endometriosis when struggling to conceive. Causes and Risk Factors The exact cause of both conditions remains a subject of medical research, but several factors play a role. Why do Fibroids Grow? Hormones (estrogen and progesterone) seem to stimulate the growth of fibroids. They often shrink after menopause when hormone levels drop. Genetics also play a part; if your mother had them, you are more likely to develop them. What Causes Endometriosis? Theories include “retrograde menstruation,” where menstrual blood flows back through the fallopian tubes into the pelvic cavity. It is also linked to immune system issues and hormonal imbalances. Consulting a Specialist Gynecologist in Aundh If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is vital to consult a qualified Gynecologist. Living in a well-connected suburb like Aundh gives you access to advanced diagnostic tools like pelvic ultrasounds and MRIs. Early intervention can prevent complications such as anemia (from heavy blood loss) or permanent pelvic scarring. A Gynecologist will perform a physical exam and may recommend laparoscopic surgery to get a definitive look at the pelvic organs. Treatment Options: From Medication to Surgery Your treatment plan depends on the severity of your symptoms and your future reproductive goals. Non-Surgical Treatments Hormonal Therapy: Birth control pills or IUDs can help manage heavy bleeding. Pain Management: Anti-inflammatory medications to reduce cramping. GnRH Agonists: Medications that temporarily “turn off” the ovaries to shrink abnormal tissue. Surgical Solutions with a Fibroid Endometriosis Surgeon in Aundh For many, surgery is the most effective way to regain quality of life. Modern techniques allow for: Myomectomy: Removing fibroids while leaving the uterus intact (ideal for those wanting children). Excision Surgery: Carefully removing endometriosis lesions to reduce pain. Hysterectomy: In severe cases, removing the uterus may be the recommended permanent solution. When to See a Doctor You should book an appointment with a fibroid endometriosis surgeon in Aundh if you notice: Periods that last longer than seven days. Pain that interferes with your daily activities or work. Difficulty getting pregnant after a year of trying. Sudden, sharp pelvic pain that does not go away. Benefits of Seeking Treatment Early Ignoring pelvic pain doesn’t make it go away; usually, it leads to more complex issues. Seeking professional care in Aundh offers several benefits: Improved Quality of Life: Get back to your routine without the “period dread.” Fertility Preservation: Early treatment of endometriosis can protect your ovarian reserve. Pain Relief: Modern surgical techniques offer faster recovery and significant pain reduction. Peace of Mind: Knowing exactly what is happening in your body reduces anxiety. Conclusion Navigating the complexities of pelvic health requires expert guidance and a compassionate approach. Whether you are dealing with the heavy bleeding of fibroids or the debilitating pain of endometriosis, relief is available right here in Pune. By consulting a trusted fibroid endometriosis surgeon in Aundh, you can receive a personalized treatment plan that addresses your specific needs and helps you reclaim your health. Don’t let pelvic pain control your life—take the first step toward a pain-free future today. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) Can you have both fibroids and endometriosis at the same time? Yes, it is quite common for women to suffer from both conditions simultaneously. This is why a thorough evaluation by a specialist is necessary. Is surgery the only option for fibroids? No. Many women manage fibroids with medication or minimally invasive procedures like Uterine Fibroid Embolization (UFE), depending on the size and location. Does endometriosis go away after menopause? While symptoms often improve when estrogen levels drop, some women continue to experience pain due to existing scar tissue or HRT (Hormone Replacement Therapy). How long is the recovery after laparoscopic surgery in Aundh? Most patients can return to light activities within 1–2 weeks, though full internal healing takes about 4–6 weeks. Can fibroids or endometriosis cause weight gain? Large fibroids can cause an increase in abdominal girth and weight. Endometriosis can cause “endo-belly” or bloating, which may feel like weight gain.